How to compute the minimum or maximum value of a field with Flink SQL
How to compute the minimum or maximum value of a field with Flink SQL
Suppose you have a topic with events that represent ticket sales of movies. In this tutorial, we'll use Flink SQL to calculate the maximum and minimum revenue of movies by year.
Setup
Let's assume the following DDL for our base movie_sales table:
CREATE TABLE movie_sales (
id INT,
title STRING,
release_year INT,
total_sales INT
);Compute min/max aggregation
Given the movie_sales table definition above, we can figure out the minimum and maximum movie revenue per year with the following aggregation:
SELECT
release_year,
MIN(total_sales) AS min_total_sales,
MAX(total_sales) AS max_total_sales
FROM movie_sales
GROUP BY release_year;Running the example
You can run the example backing this tutorial in one of three ways: a Flink Table API-based JUnit test, locally with the Flink SQL Client against Flink and Kafka running in Docker, or with Confluent Cloud.
Flink Table API-based test
Prerequisites
- Java 17, e.g., follow the OpenJDK installation instructions here if you don't have Java.
- Docker running via Docker Desktop or Docker Engine
Run the test
Clone the confluentinc/tutorials GitHub repository (if you haven't already) and navigate to the tutorials directory:
git clone git@github.com:confluentinc/tutorials.git
cd tutorialsRun the following command to execute FlinkSqlAggregatingMinMaxTest#testMinMax:
./gradlew clean :aggregating-minmax:flinksql:testThe test starts Kafka and Schema Registry with Testcontainers, runs the Flink SQL commands above against a local Flink StreamExecutionEnvironment, and ensures that the aggregation results are what we expect.
Flink SQL Client CLI
Prerequisites
- Docker running via Docker Desktop or Docker Engine
- Docker Compose. Ensure that the command docker compose version succeeds.
Run the commands
Clone the confluentinc/tutorials GitHub repository (if you haven't already) and navigate to the tutorials directory:
git clone git@github.com:confluentinc/tutorials.git
cd tutorialsStart Flink and Kafka:
docker compose -f ./docker/docker-compose-flinksql.yml up -dNext, open the Flink SQL Client CLI:
docker exec -it flink-sql-client sql-client.shFinally, run following SQL statements to create the movie_sales table backed by Kafka running in Docker, populate it with test data, and run the aggregating min/max query.
CREATE TABLE movie_sales (
id INT,
title STRING,
release_year INT,
total_sales INT
) WITH (
'connector' = 'kafka',
'topic' = 'movie-sales',
'properties.bootstrap.servers' = 'broker:9092',
'scan.startup.mode' = 'earliest-offset',
'key.format' = 'raw',
'key.fields' = 'id',
'value.format' = 'avro-confluent',
'value.avro-confluent.url' = 'http://schema-registry:8081',
'value.fields-include' = 'EXCEPT_KEY'
);
INSERT INTO movie_sales VALUES
(0, 'Avengers: Endgame', 2019, 856980506),
(1, 'Captain Marvel', 2019, 426829839),
(2, 'Toy Story 4', 2019, 401486230),
(3, 'The Lion King', 2019, 385082142),
(4, 'Black Panther', 2018, 700059566),
(5, 'Avengers: Infinity War', 2018, 678815482),
(6, 'Deadpool 2', 2018, 324512774),
(7, 'Beauty and the Beast', 2017, 517218368),
(8, 'Wonder Woman', 2017, 412563408),
(9, 'Star Wars Ep. VIII: The Last Jedi', 2017, 517218368);SELECT
release_year,
MIN(total_sales) AS min_total_sales,
MAX(total_sales) AS max_total_sales
FROM movie_sales
GROUP BY release_year;The query output should look like this:
release_year min_total_sales max_total_sales
2017 412563408 517218368
2019 385082142 856980506
2018 324512774 700059566When you are finished, clean up the containers used for this tutorial by running:
docker compose -f ./docker/docker-compose-flinksql.yml downConfluent Cloud
Prerequisites
- A Confluent Cloud account
- A Flink compute pool created in Confluent Cloud. Follow this quick start to create one.
Run the commands
In the Confluent Cloud Console, navigate to your environment and then click the Open SQL Workspace button for the compute pool that you have created.
Select the default catalog (Confluent Cloud environment) and database (Kafka cluster) to use with the dropdowns at the top right.
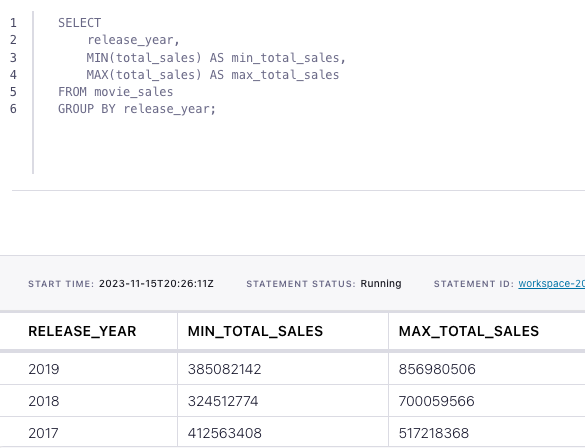
Finally, run following SQL statements to create the movie_sales table, populate it with test data, and run the aggregating min/max query.
CREATE TABLE movie_sales (
id INT,
title STRING,
release_year INT,
total_sales INT
);INSERT INTO movie_sales VALUES
(0, 'Avengers: Endgame', 2019, 856980506),
(1, 'Captain Marvel', 2019, 426829839),
(2, 'Toy Story 4', 2019, 401486230),
(3, 'The Lion King', 2019, 385082142),
(4, 'Black Panther', 2018, 700059566),
(5, 'Avengers: Infinity War', 2018, 678815482),
(6, 'Deadpool 2', 2018, 324512774),
(7, 'Beauty and the Beast', 2017, 517218368),
(8, 'Wonder Woman', 2017, 412563408),
(9, 'Star Wars Ep. VIII: The Last Jedi', 2017, 517218368);SELECT
release_year,
MIN(total_sales) AS min_total_sales,
MAX(total_sales) AS max_total_sales
FROM movie_sales
GROUP BY release_year;The query output should look like this: