How to join two streams of data with Flink SQL
How to join two streams of data with Flink SQL
Suppose you have two streams containing events for orders and shipments. In this tutorial, we'll use Flink SQL to join these two streams to create a new, enriched one. The new stream will tell us which orders have been successfully shipped, how long it took for them to ship, and the warehouse from which they shipped.
Setup
Let's assume the following DDL for our base orders and shipments tables:
CREATE TABLE orders (
id INT,
total_amount DOUBLE,
customer_name VARCHAR,
order_ts_raw BIGINT
);CREATE TABLE shipments (
id VARCHAR,
order_id INT,
warehouse VARCHAR,
ship_ts_raw BIGINT
);Note that we are using order_ts_raw and ship_ts_raw as records timestamp in these tables. This is going to be important later on when we write queries that need to know about the time each event occurred at. By using a field of the event, we can process the events at any time and get a deterministic result. This is known as event time.
Join event streams
Given the orders and shipments table definitions above, let’s join these event streams together to gain some insight into the order-to-shipping process. Then we’ll discuss some of the concepts used in the query to enable retrieving your desired results.
SELECT o.id as order_id,
FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw) as ORDER_TS,
o.total_amount as TOTAL,
o.customer_name as CUSTOMER,
s.id as SHIP_ID,
FROM_UNIXTIME(s.ship_ts_raw) as SHIP_TS,
s.warehouse,
TIMESTAMPDIFF(HOUR,
TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw)),
TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(s.ship_ts_raw))) as HR_TO_SHIP
FROM orders o
INNER JOIN shipments s
ON o.id = s.order_id
AND TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(s.ship_ts_raw))
BETWEEN TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw))
AND TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw)) + INTERVAL '7' DAY;
Earlier we talked about the event timestamps stored as a BIGINT type which is great for flexibity, but hard to read and interpret. So to address that issue we used the FROM_UNIXTIME function for both the order and shipment timestamp. FROM_UNIXTIME converts a numeric type (an epoch based timestamp in this case) to a formatted string in the default format of yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss, which is now an easily understood format.
We also used additional temporal functions, TO_TIMESTAMP, TIMESTAMPDIFF, and INTERVAL. TO_TIMESTAMP converts a date string, like the one returned from TO_TIMESTAMP into a timestamp suitable for other functions such as TIMESTAMPDIFF and INTERVAL. We used TIMESTAMPDIFF to calculate the difference, in hours, between accepting the order and shipping to the customer.
The query we issued performs an inner join between the orders and shipments. This kind of join only emits events when there’s a match on the criteria of both sides of the join. In effect, this only joins orders that have successfully shipped. Additionally, we used the INTERVAL function to perform an interval join, which also needs a SQL timestamp to specify an addition join requirement that order and shipment occurred within seven days of each other.
Running the example
You can run the example backing this tutorial in one of three ways: a Flink Table API-based JUnit test, locally with the Flink SQL Client against Flink and Kafka running in Docker, or with Confluent Cloud.
Flink Table API-based test
Prerequisites
- Java 17, e.g., follow the OpenJDK installation instructions here if you don't have Java.
- Docker running via Docker Desktop or Docker Engine
Run the test
Clone the confluentinc/tutorials GitHub repository (if you haven't already) and navigate to the tutorials directory:
git clone git@github.com:confluentinc/tutorials.git
cd tutorialsRun the following command to execute FlinkSqlIntervalJoinTest#testJoin:
./gradlew clean :joining-stream-stream:flinksql:testThe test starts Kafka and Schema Registry with Testcontainers, runs the Flink SQL commands above against a local Flink StreamExecutionEnvironment, and ensures that the join results are what we expect.
Flink SQL Client CLI
Prerequisites
- Docker running via Docker Desktop or Docker Engine
- Docker Compose. Ensure that the command docker compose version succeeds.
Run the commands
Clone the confluentinc/tutorials GitHub repository (if you haven't already) and navigate to the tutorials directory:
git clone git@github.com:confluentinc/tutorials.git
cd tutorialsStart Flink and Kafka:
docker compose -f ./docker/docker-compose-flinksql.yml up -dNext, open the Flink SQL Client CLI:
docker exec -it flink-sql-client sql-client.shFinally, run following SQL statements to create the orders and shipments tables backed by Kafka running in Docker, populate them with test data, and run the join query.
CREATE TABLE orders (
id INT,
total_amount DOUBLE,
customer_name VARCHAR,
order_ts_raw BIGINT
) WITH (
'connector' = 'kafka',
'topic' = 'orders',
'properties.bootstrap.servers' = 'broker:9092',
'scan.startup.mode' = 'earliest-offset',
'key.format' = 'raw',
'key.fields' = 'id',
'value.format' = 'avro-confluent',
'value.avro-confluent.url' = 'http://schema-registry:8081',
'value.fields-include' = 'EXCEPT_KEY'
);CREATE TABLE shipments (
id VARCHAR,
order_id INT,
warehouse VARCHAR,
ship_ts_raw BIGINT
) WITH (
'connector' = 'kafka',
'topic' = 'shipments',
'properties.bootstrap.servers' = 'broker:9092',
'scan.startup.mode' = 'earliest-offset',
'key.format' = 'raw',
'key.fields' = 'id',
'value.format' = 'avro-confluent',
'value.avro-confluent.url' = 'http://schema-registry:8081',
'value.fields-include' = 'EXCEPT_KEY'
);INSERT INTO orders
VALUES ( 1, 404.89, 'Art Vandelay', 1692812175),
( 2, 50.45, 'Bob Sacamanto', 1692826575),
( 3, 113.23, 'Bilbo Baggins', 1692826575),
( 4, 90.43, 'Harry Potter', 1692812175),
( 5, 495.22, 'John Hechinger', 1692819375),
( 6, 410.13, 'Mandelorean', 1692826575),
( 7, 333.84, 'Jane Smith', 1692822975),
( 8, 26.14, 'HJ Pennypacker' , 1692819375),
( 9, 450.77, 'Colonel Mustard', 1692812175),
( 10,195.13, 'Prof. Jones', 1692822975);INSERT INTO shipments
VALUES ('shipment_1', 1, 'Bar Harbor', 1692815775),
('shipment_2', 2, 'Boston', 1692851775),
('shipment_3', 3, 'Providence', 1692851775),
('shipment_4', 4, 'Springfield', 1692826575),
('shipment_5', 5, 'Bar Harbor', 1692822975),
('shipment_6', 6, 'Boston', 1692851775),
('shipment_7', 7, 'Jackson Hole', 1692840975),
('shipment_8', 8, 'Whitefish' , 1692822975),
('shipment_9', 9, 'Jackson Hole', 1692984975),
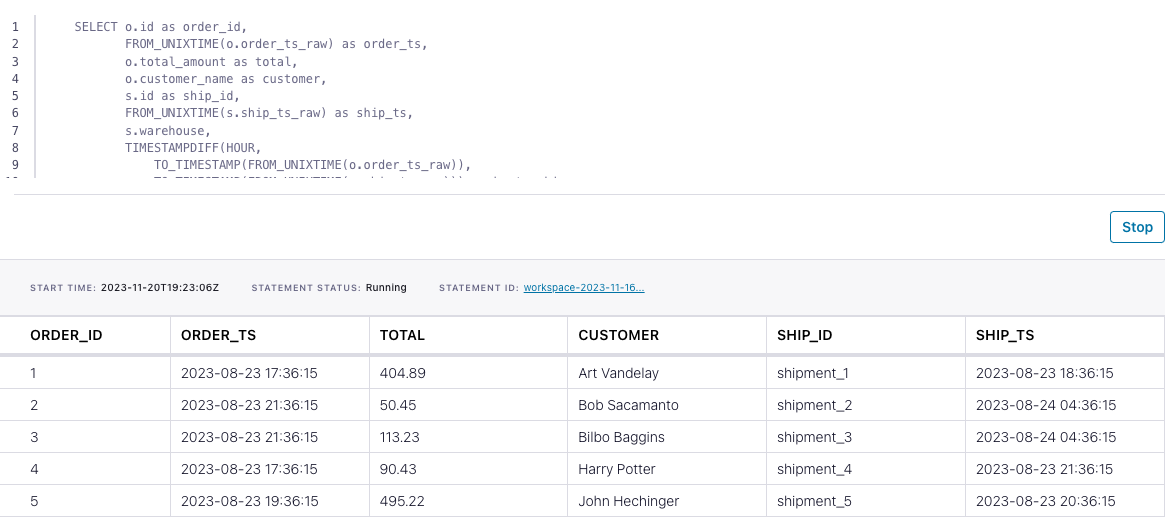
('shipment_10', 10, 'Columbia Falls', 1692984975);SELECT o.id as order_id,
FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw) as order_ts,
o.total_amount as total,
o.customer_name as customer,
s.id as ship_id,
FROM_UNIXTIME(s.ship_ts_raw) as ship_ts,
s.warehouse,
TIMESTAMPDIFF(HOUR,
TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw)),
TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(s.ship_ts_raw))) as hr_to_ship
FROM orders o
INNER JOIN shipments s
ON o.id = s.order_id
AND TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(s.ship_ts_raw))
BETWEEN TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw))
AND TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw)) + INTERVAL '7' DAY;The query output should look like this:
order_id order_ts total customer ship_id ship_ts warehouse hr_to_ship
1 2023-08-23 17:36:15 404.89 Art Vandelay shipment_1 2023-08-23 18:36:15 Bar Harbor 1
2 2023-08-23 21:36:15 50.45 Bob Sacamanto shipment_2 2023-08-24 04:36:15 Boston 7
3 2023-08-23 21:36:15 113.23 Bilbo Baggins shipment_3 2023-08-24 04:36:15 Providence 7
4 2023-08-23 17:36:15 90.43 Harry Potter shipment_4 2023-08-23 21:36:15 Springfield 4
5 2023-08-23 19:36:15 495.22 John Hechinger shipment_5 2023-08-23 20:36:15 Bar Harbor 1
6 2023-08-23 21:36:15 410.13 Mandelorean shipment_6 2023-08-24 04:36:15 Boston 7
7 2023-08-23 20:36:15 333.84 Jane Smith shipment_7 2023-08-24 01:36:15 Jackson Hole 5
8 2023-08-23 19:36:15 26.14 HJ Pennypacker shipment_8 2023-08-23 20:36:15 Whitefish 1
9 2023-08-23 17:36:15 450.77 Colonel Mustard shipment_9 2023-08-25 17:36:15 Jackson Hole 48
10 2023-08-23 20:36:15 195.13 Prof. Jones shipment_10 2023-08-25 17:36:15 Columbia Falls 45When you are finished, clean up the containers used for this tutorial by running:
docker compose -f ./docker/docker-compose-flinksql.yml downConfluent Cloud
Prerequisites
- A Confluent Cloud account
- A Flink compute pool created in Confluent Cloud. Follow this quick start to create one.
Run the commands
In the Confluent Cloud Console, navigate to your environment and then click the Open SQL Workspace button for the compute pool that you have created.
Select the default catalog (Confluent Cloud environment) and database (Kafka cluster) to use with the dropdowns at the top right.
Finally, run following SQL statements to create the orders and shipments tables, populate them with test data, and run the join query.
CREATE TABLE orders (
id INT,
total_amount DOUBLE,
customer_name VARCHAR,
order_ts_raw BIGINT
);CREATE TABLE shipments (
id VARCHAR,
order_id INT,
warehouse VARCHAR,
ship_ts_raw BIGINT
);INSERT INTO orders
VALUES ( 1, 404.89, 'Art Vandelay', 1692812175),
( 2, 50.45, 'Bob Sacamanto', 1692826575),
( 3, 113.23, 'Bilbo Baggins', 1692826575),
( 4, 90.43, 'Harry Potter', 1692812175),
( 5, 495.22, 'John Hechinger', 1692819375),
( 6, 410.13, 'Mandelorean', 1692826575),
( 7, 333.84, 'Jane Smith', 1692822975),
( 8, 26.14, 'HJ Pennypacker' , 1692819375),
( 9, 450.77, 'Colonel Mustard', 1692812175),
( 10,195.13, 'Prof. Jones', 1692822975);INSERT INTO shipments
VALUES ('shipment_1', 1, 'Bar Harbor', 1692815775),
('shipment_2', 2, 'Boston', 1692851775),
('shipment_3', 3, 'Providence', 1692851775),
('shipment_4', 4, 'Springfield', 1692826575),
('shipment_5', 5, 'Bar Harbor', 1692822975),
('shipment_6', 6, 'Boston', 1692851775),
('shipment_7', 7, 'Jackson Hole', 1692840975),
('shipment_8', 8, 'Whitefish' , 1692822975),
('shipment_9', 9, 'Jackson Hole', 1692984975),
('shipment_10', 10, 'Columbia Falls', 1692984975);SELECT o.id as order_id,
FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw) as order_ts,
o.total_amount as total,
o.customer_name as customer,
s.id as ship_id,
FROM_UNIXTIME(s.ship_ts_raw) as ship_ts,
s.warehouse,
TIMESTAMPDIFF(HOUR,
TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw)),
TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(s.ship_ts_raw))) as hr_to_ship
FROM orders o
INNER JOIN shipments s
ON o.id = s.order_id
AND TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(s.ship_ts_raw))
BETWEEN TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw))
AND TO_TIMESTAMP(FROM_UNIXTIME(o.order_ts_raw)) + INTERVAL '7' DAY;The query output should look like this: