Data Mesh
Learn about building a data mesh on event streams with Apache Kafka® and Confluent.
What Is Data Mesh?
Data mesh is a concept that ensures data access, governance, federation, and interoperability across distributed teams and systems. It is a new approach for designing modern data architectures, based on four principles:
- Domain ownership: Responsibility over modeling and providing important data is distributed to the people closest to it, providing access to the exact data they need, when they need it.
- Data as a product: Data is treated as a product like any other, complete with a data product owner, consumer consultations, release cycles, and quality and service-level agreements.
- Self-service: Empower consumers to independently search, discover, and consume data products. Data product owners are provided standardized tools for populating and publishing their data product.
- Federated governance: This is embodied by a cross-organization team that provides global standards for the formats, modes, and requirements of publishing and using data products. This team must maintain the delicate balance between centralized standards for compatibility and decentralized autonomy for true domain ownership.
To learn more, we recommend you check out these three important resources.
Read about it
Check out Adam Bellemare's Practical Data Mesh ebook.

Learn about it
Learn about Data Mesh with Data Mesh 101 on developer.confluent.io.

Try it out
The Definitive Guide to Building a Data Mesh with Event Streams blog post provides a summary of the foundational concepts and includes a data mesh prototype that you can build and run yourself.
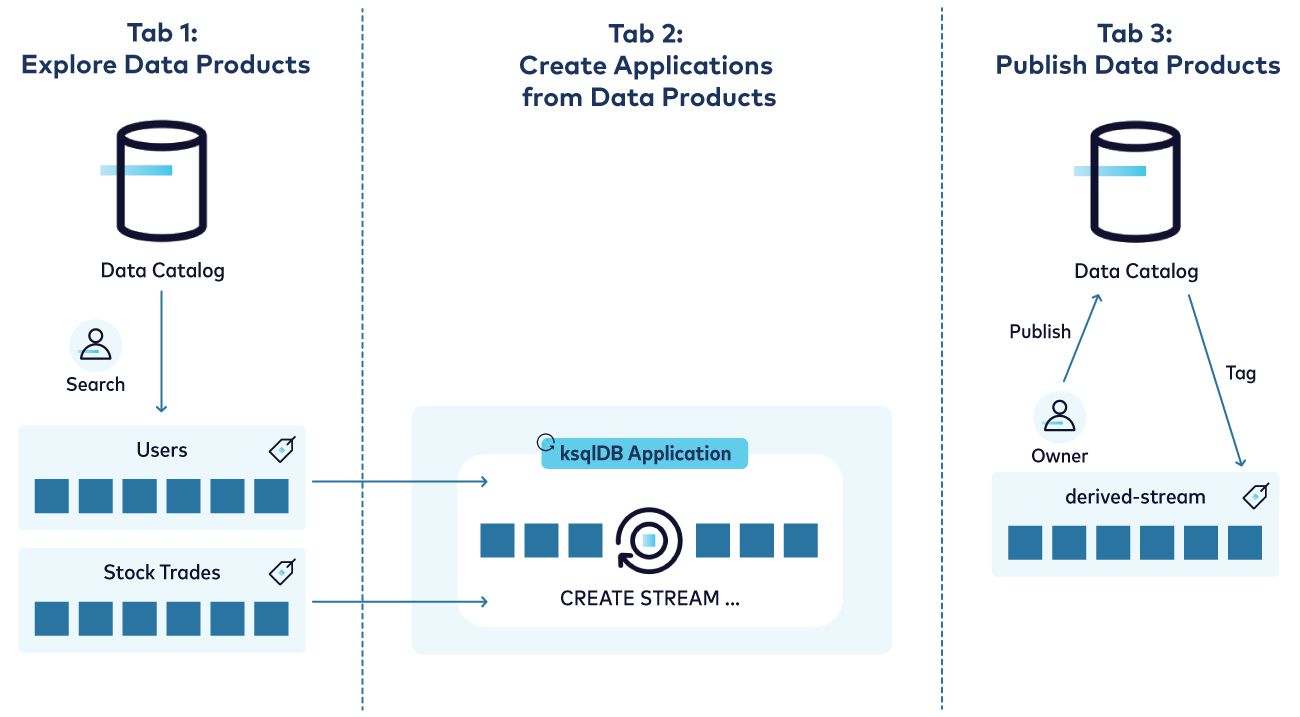
The data mesh prototype is built on Confluent Cloud using event streams, ksqlDB, and the fully managed data catalog API. The prototype's GitHub repository has all the details.
Why a Data Mesh?
First introduced by Zhamak Dehghani in How to Move Beyond a Monolithic Data Lake to a Distributed Data Mesh, data mesh aims to solve scaling failures in centralized approaches in data systems. As companies become software, there is a general trend towards decentralized data ownership to enable scale.
Data mesh solves a number of common problems. At the smaller scale, it addresses many of the issues seen with data pipelines, which often become brittle and problematic over time by creating their own webs and messy point-to-point kind of systems.
It also addresses larger organizational issues, such as different departments in a company disagreeing on core facts of the business. In a data mesh, you’re less likely to have copies of facts. In both of these cases, a data mesh can bring much needed order to a system, resulting in a more mature, manageable, and evolvable data architecture.
More Data Mesh Resources
- Watch Zhamak Dehghani in How to Build the Data Mesh Foundation: A Principled Approach at Kafka Summit Europe 2021
- Watch Apache Kafka and the Data Mesh to learn about the differences between streams and centralized approaches to data mesh
- Read Saxo Bank's blog post: Best Practices for a Distributed Domain-Driven Architecture
- Watch Gloo.us present How a Data Mesh Is Driving Our Platform at Kafka Summit Americas 2021
- Read An Introduction to Data Mesh
- Dive deeper into these principles and the data mesh architectural paradigm shift on the Streaming Audio podcast with Zhamak Dehghani and Tim Berglund
- Learn more about Data Mesh Architecture: A Modern Distributed Data Model, also on the Streaming Audio podcast
Reach Out
Want to learn more about data mesh and how to use it? For questions, feedback, or to open a discussion on data mesh, sign up and engage with the friendly Confluent Community. For more resources like this, be sure to explore all of Confluent Developer and find complete courses, tutorials, examples, and more.
