Hands On: Filtering Streams of Data with ksqlDB

Tim Berglund
VP Developer Relations
Hands On: Filtering Streams of Data with ksqlDB
The ratings messages that we receive include a field that indicates the device from which they were left. The field is called channel and includes some values indicating that they’re from test devices.
We’d like to create a new stream that includes only data from live devices. For this we can use ksqlDB.
-
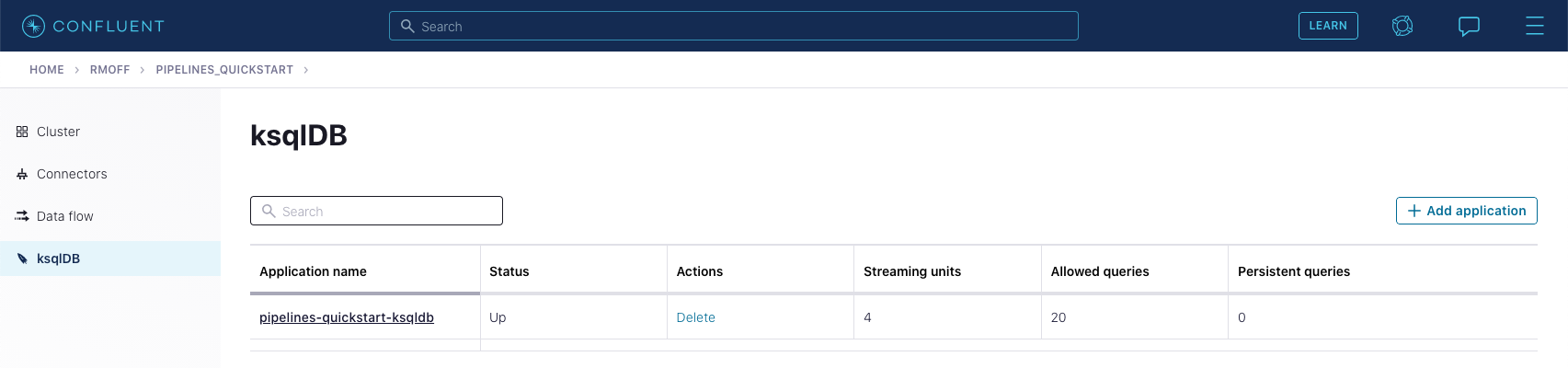
Before continuing, make sure that you have created a ksqlDB application on Confluent Cloud as described in the first exercise. From the "ksqlDB" page, you should see the application listed and in "Status" Up.
-
Click on the ksqlDB application to open the editor. The first thing that you need to do is to declare a ksqlDB stream on the topic that holds the ratings events. This gives ksqlDB the information that it needs about the schema of the data.
Paste the following statement into the "Editor" and click Run query.
CREATE STREAM RATINGS WITH (KAFKA_TOPIC='ratings',VALUE_FORMAT='AVRO');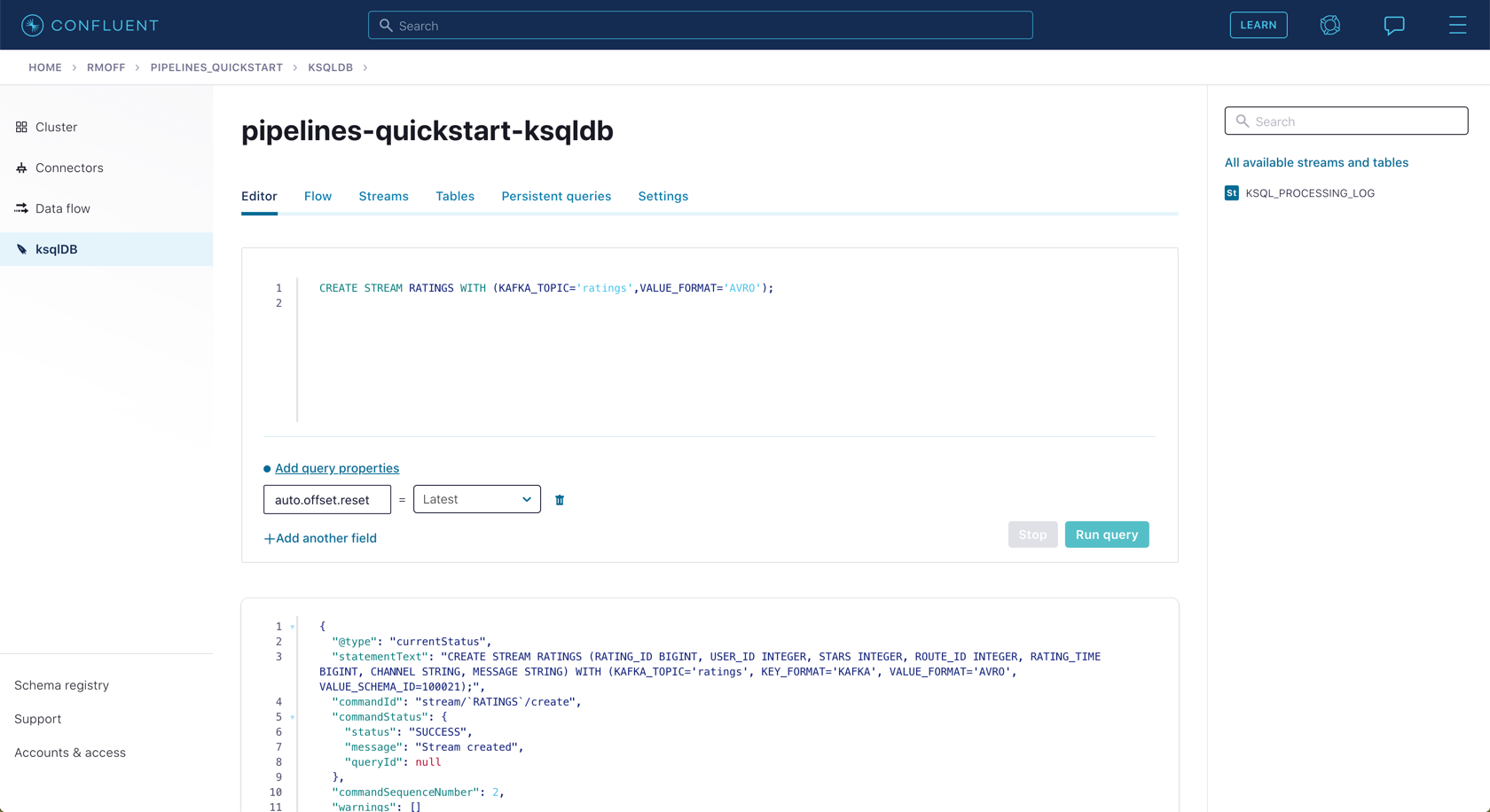
-
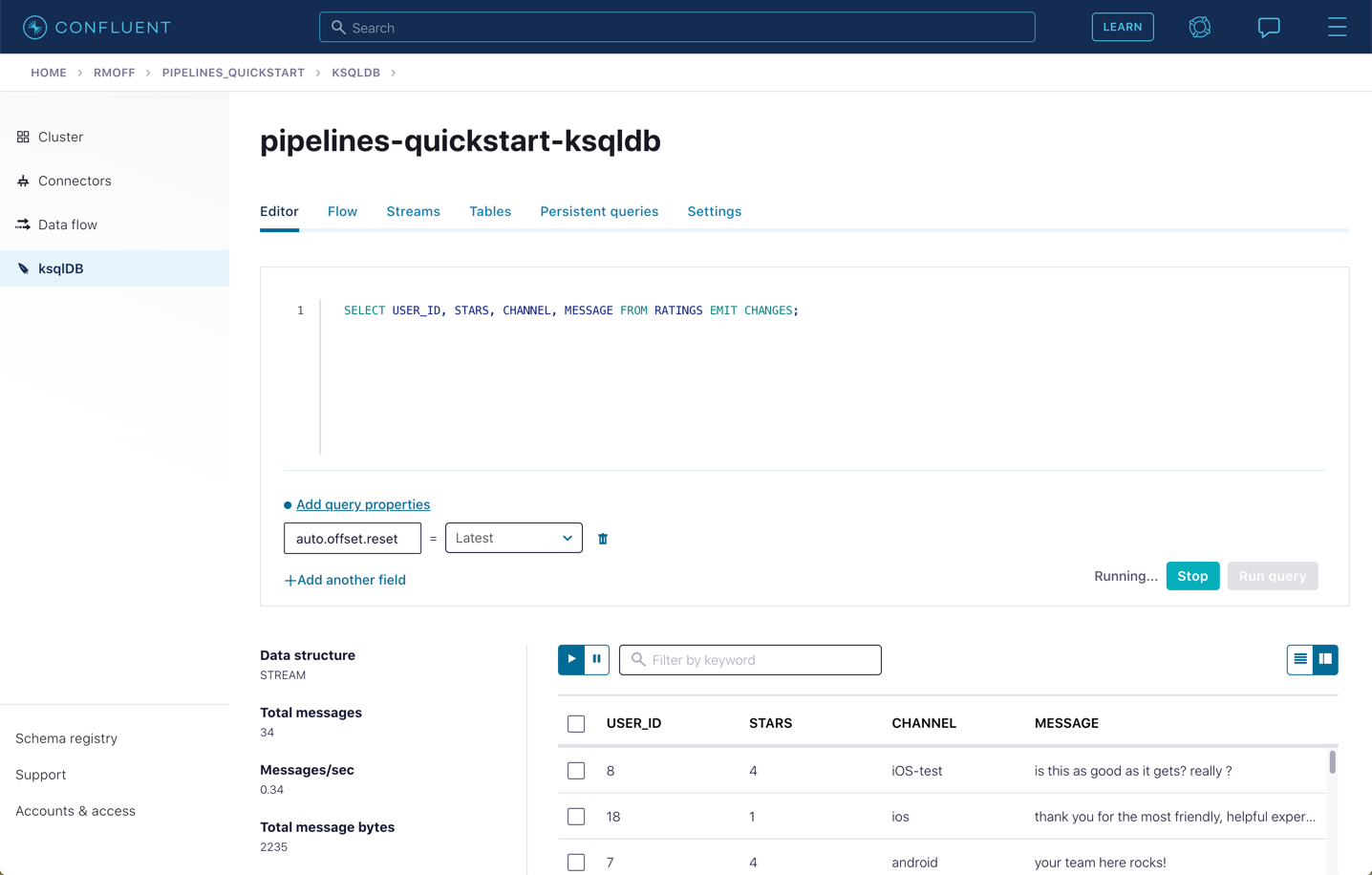
You can view the messages flowing through the Kafka topic by running a SELECT against the stream:
SELECT USER_ID, STARS, CHANNEL, MESSAGE FROM RATINGS EMIT CHANGES;Use the table icon in to the top right of the messages to view them as columns
-
Note how in the data shown returned in the above query, there are values in the CHANNEL field that include -test. You can filter these out using a SQL predicate:
SELECT USER_ID, STARS, CHANNEL, MESSAGE FROM RATINGS WHERE LCASE(CHANNEL) NOT LIKE '%test%' EMIT CHANGES;When you run this, you’ll notice that the results are returned to the screen.
-
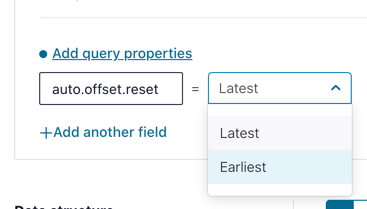
To tell ksqlDB to process all of the existing messages in the topic as well as all new ones that arrive, we set the auto.offset.reset parameter to earliest. To do this, change the dropdown from its default of Latest to Earliest.
-
Using the above statement, we can get ksqlDB to write all messages matching this criterion into a new ksqlDB stream. A ksqlDB stream is always backed by a Kafka topic.
CREATE STREAM RATINGS_LIVE AS SELECT * FROM RATINGS WHERE LCASE(CHANNEL) NOT LIKE '%test%' EMIT CHANGES;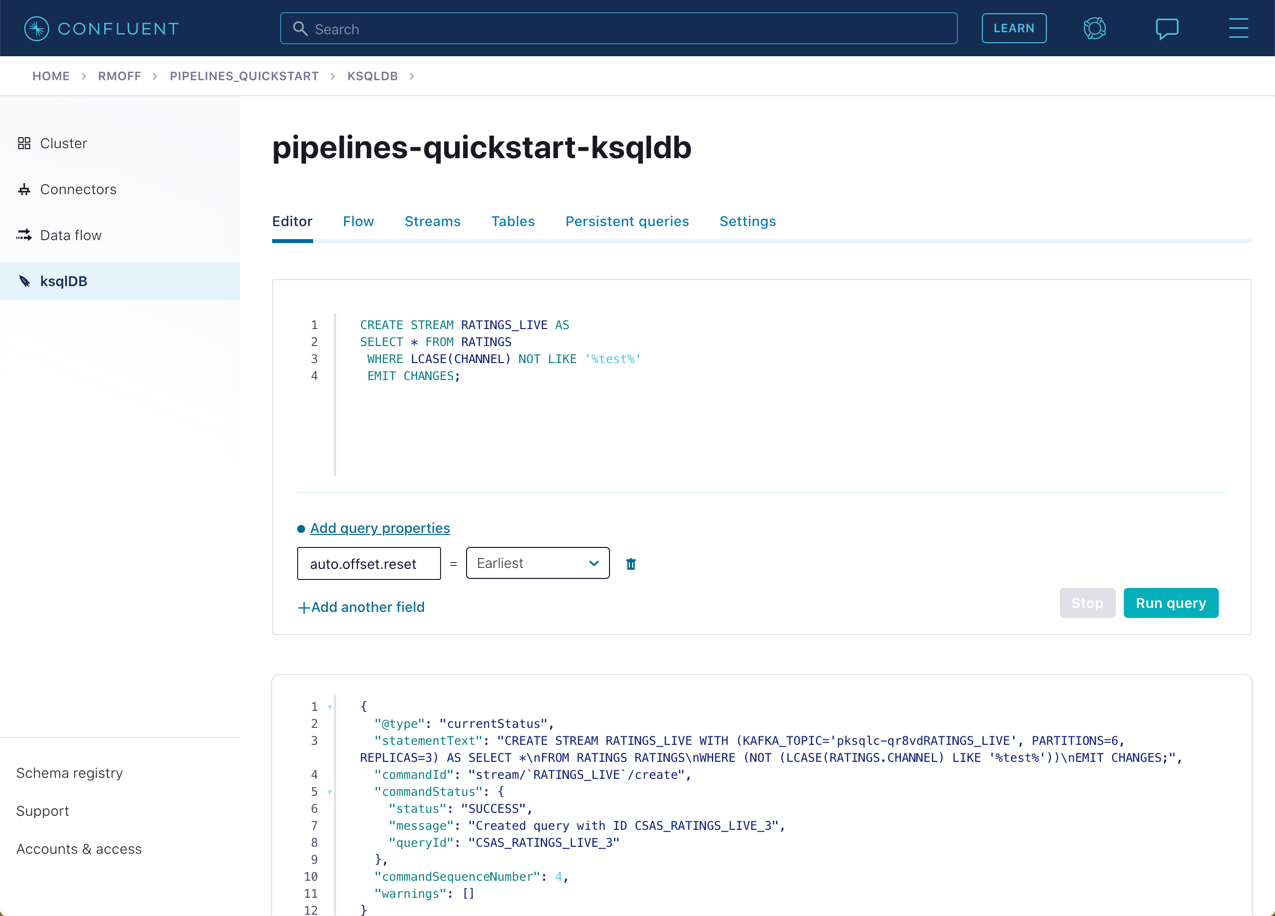
-
Query the new stream and validate that there are no CHANNEL values with test in them:
SELECT USER_ID, STARS, CHANNEL, MESSAGE FROM RATINGS_LIVE EMIT CHANGES;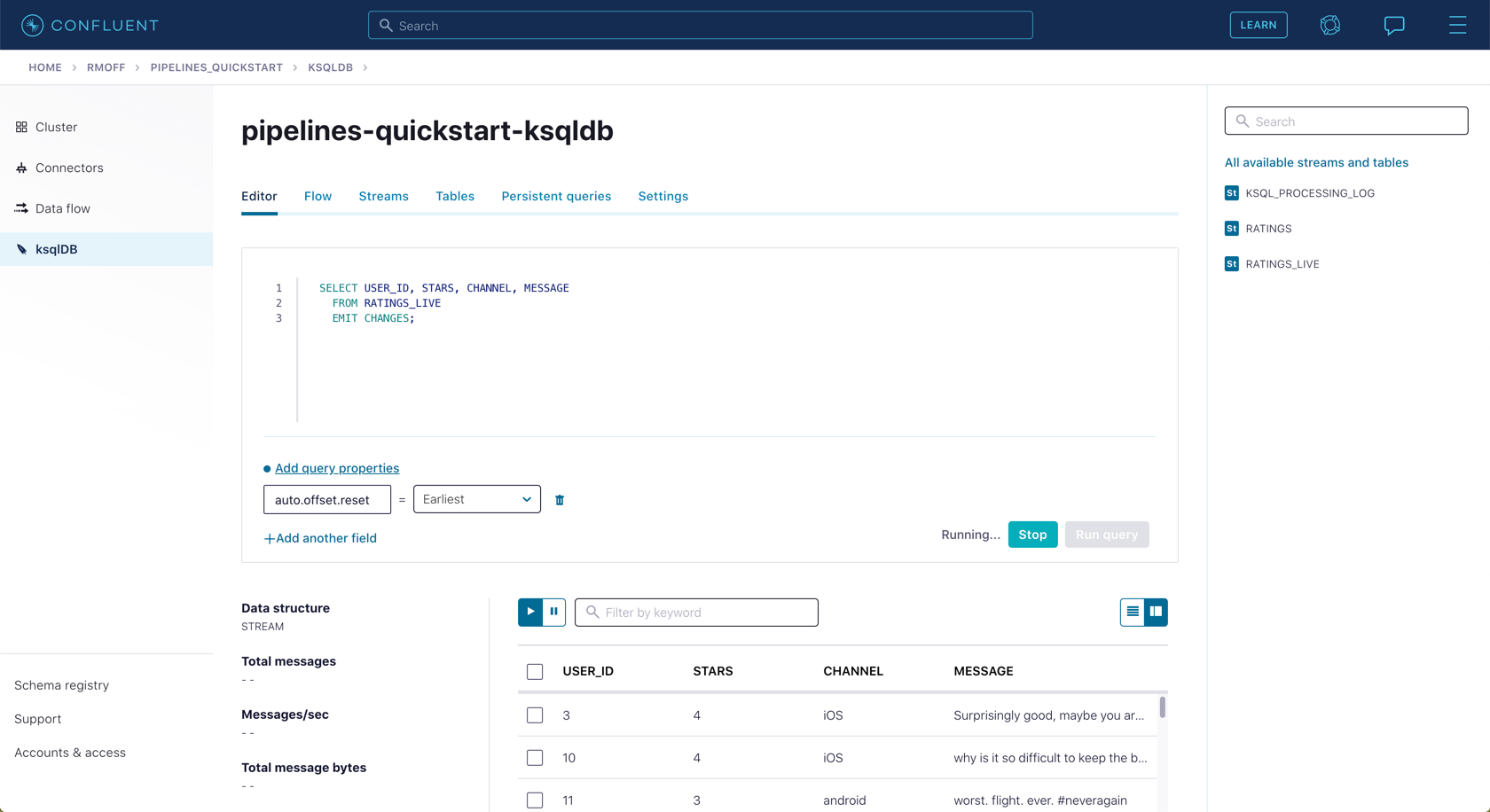
-
From your cluster’s "Topics" page, locate the new Kafka topic that’s been created. It will have a prefix in its name but end with RATINGS_LIVE.
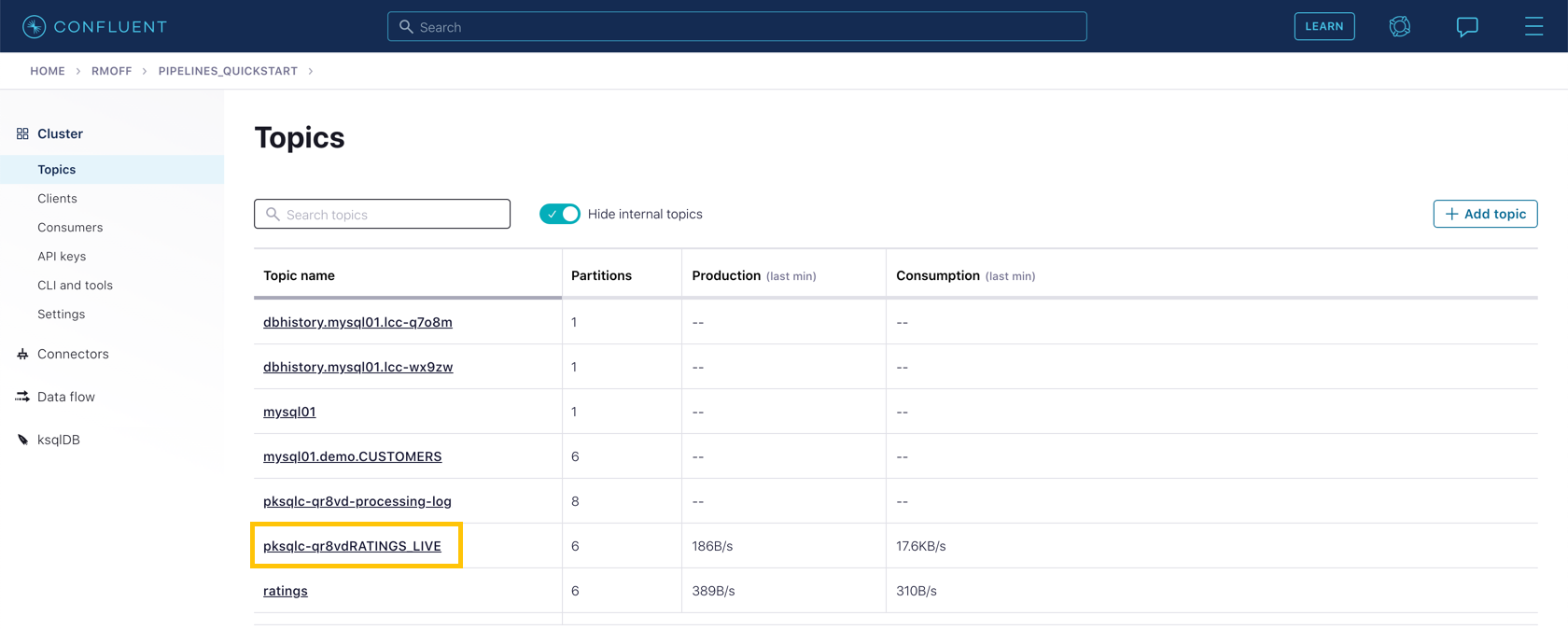
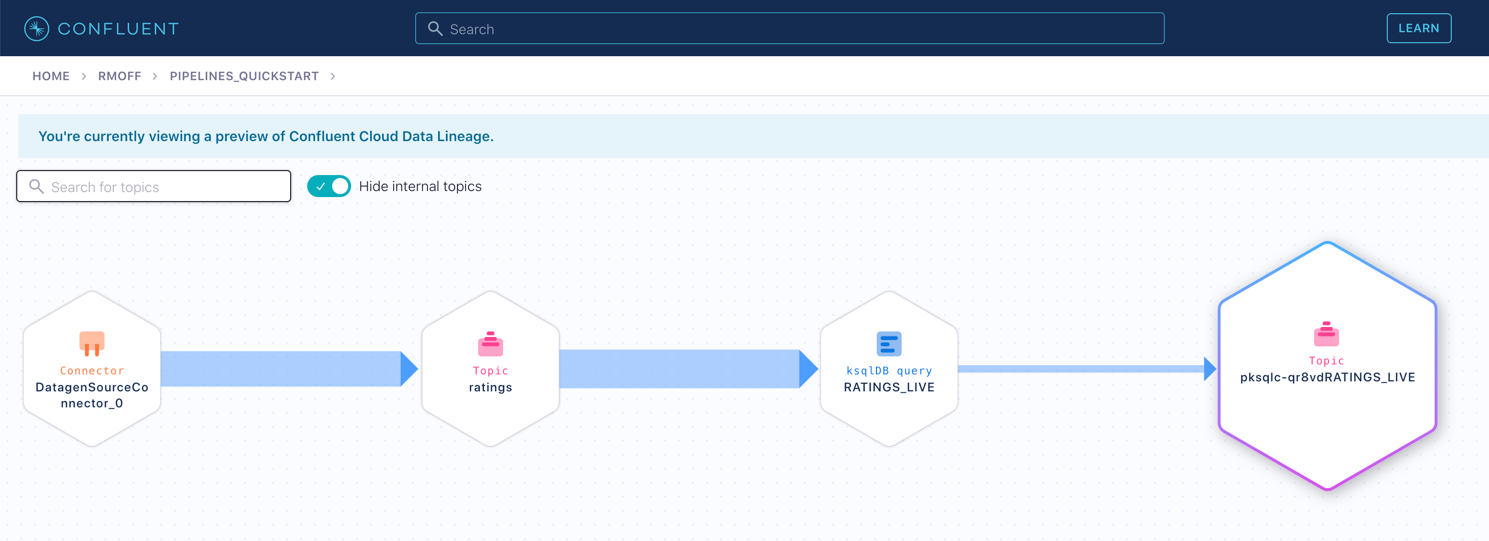
Click on the topic. If data lineage is enabled on your cluster, click on it to view the flow of data that you’ve created.
Use the promo code PIPELINES101 & CONFLUENTDEV1 to get $25 of free Confluent Cloud usage and skip credit card entry.
Hands On: Filtering Streams of Data with ksqlDB
Let's put filtering into practice in this exercise. The ratings messages that we get from our handy-dandy datagen connector includes a field that indicates the fictional device from which they fictionally originated. That field is called channel, and it includes some values indicating that they're from test devices. We want to filter those out. We're gonna create a stream processor to do that. So, from your cluster's main page, launch the ksqlDB application. The first thing is to create a stream on the ratings topic. Now stream is an abstraction on top of a topic, is a way of wrapping that topic and say, "Hey ksqlDB, this is a thing for you. This is the schema, this is its name, and it should be a part of your world". Yes, there's a topic underneath it. but now, to ksqlDB, it is this abstraction called the stream. Query the stream to make sure that the data is there. This is always a good sanity check. Make a stream, do a select, make sure that you can see things in it for a warm fuzzy. Because there's a schema, we can even project certain fields. So toggle the output to see it as a table. Note, the test values in the channel field, we wanna filter those out. Let's use some SQL to filter the data here. Here we're using a where clause to define that filter predicate. I trust I don't need to do too much explaining of that. We're gonna force the channel field to lowercase also, 'cause who knows, and then compare it to the wild cart pattern you see here being a little bit fancy. Run the query and see how the channel values are now only those which don't have test in the text. Using the SQL you've just prototyped in the editor. Now we're going to do a create stream. We're gonna prefix it with create stream, to tell ksqlDB to write the results of this query to a new Kafka topic, to create a new stream with those results. Before we run it, we're gonna tell ksqlDB to read all the data from the beginning of the topic by setting good old auto off set reset to earliest. Now click on run query. And the query is running. Now that we have a new stream, we can query it just like the original ratings one. The difference this time is the messages are only those which aren't test messages. Yes, friends, we can write SQL and we can put a predicate in a where clause. This is a minor victory. We can reassure ourselves that this ksqlDB stream is creating and populating a new Kafka topic by heading over to the topics tab. And look there that the ratings live topic exists with that silly prefix that you see there, that's system generated Click on the topic, and if you've got data lineage on your environment view, you can see the flow of the data from data generator, into the source topic processed by ksqlDB and in to a new topic. And with that, you have filtered data using ksqlDB.
Be the first to get updates and new content
We will only share developer content and updates, including notifications when new content is added. We will never send you sales emails. 🙂 By subscribing, you understand we will process your personal information in accordance with our Privacy Statement.








