Hands On: Joining Data Streams with ksqlDB

Tim Berglund
VP Developer Relations
Hands On: Joining Data Streams with ksqlDB
In the previous exercise, we filtered a stream of ratings events to create a new one that excluded test messages. Now we’re going to use the customer information that we are pulling in from an external MySQL database to enrich each rating as it arrives (as well as all the existing ratings that we have already received and are storing on the Kafka topic).
To do this, we need to first model the customer data held in the Kafka topic in such a way that ksqlDB can use it to join to the ratings events. We’ll do this by creating a ksqlDB table (rather than a stream as done for the events).
-
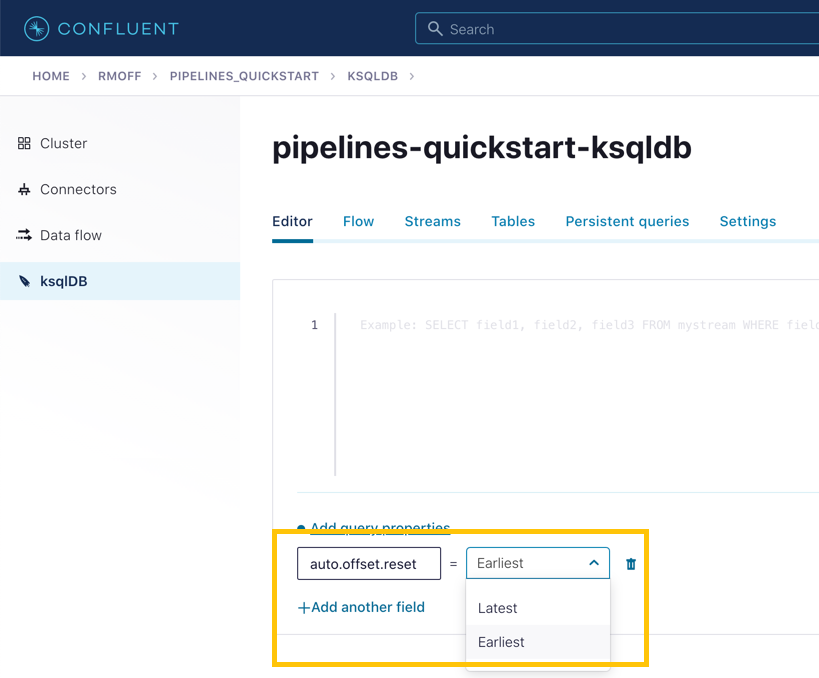
To start with, we need to pre-process the customer data to make the primary key field accessible. Because we need to process all of the data in the topic, it’s important that we set auto.offset.reset to earliest. If you don’t do this, then you’ll get no data in the resulting stream.
In the Confluent Cloud ksqlDB editor, use the drop-down menu to set auto.offset.reset to earliest.
Now run the following SQL:
CREATE STREAM CUSTOMERS_S WITH (KAFKA_TOPIC ='mysql01.demo.CUSTOMERS', KEY_FORMAT ='JSON', VALUE_FORMAT='AVRO');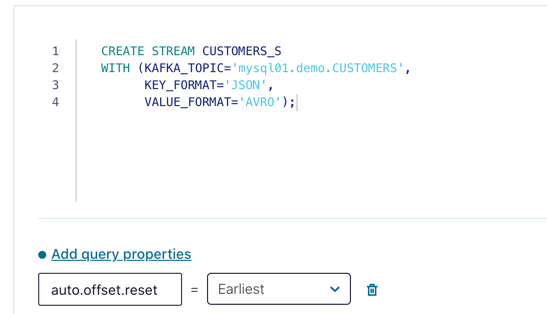
-
Now create a ksqlDB table on the customer data. A ksqlDB table is built on a stream and returns the value for a given key. If there are two messages with the same key, the table will have one entry (rather than two, as in a stream).
Run the following SQL, making sure that as before, auto.offset.reset is set to earliest.
CREATE TABLE CUSTOMERS WITH (FORMAT='AVRO') AS SELECT id AS customer_id, LATEST_BY_OFFSET(first_name) AS first_name, LATEST_BY_OFFSET(last_name) AS last_name, LATEST_BY_OFFSET(email) AS email, LATEST_BY_OFFSET(club_status) AS club_status FROM CUSTOMERS_S GROUP BY id; -
With the table created, you can now enrich the ratings events with information about the customer, using the primary/foreign key relationship.
Run the following SQL to perform a join between the stream of ratings and the table of customer details. Note that the optional KAFKA_TOPIC parameter is specified to set the name of the Kafka topic to which the results are written.
CREATE STREAM RATINGS_WITH_CUSTOMER_DATA WITH (KAFKA_TOPIC='ratings-enriched') AS SELECT C.CUSTOMER_ID, C.FIRST_NAME + ' ' + C.LAST_NAME AS FULL_NAME, C.CLUB_STATUS, C.EMAIL, R.RATING_ID, R.MESSAGE, R.STARS, R.CHANNEL, TIMESTAMPTOSTRING(R.ROWTIME,'yyyy-MM-dd''T''HH:mm:ss.SSSZ') AS RATING_TS FROM RATINGS_LIVE R INNER JOIN CUSTOMERS C ON R.USER_ID = C.CUSTOMER_ID EMIT CHANGES; -
Query the newly created stream:
SELECT * FROM RATINGS_WITH_CUSTOMER_DATA EMIT CHANGES;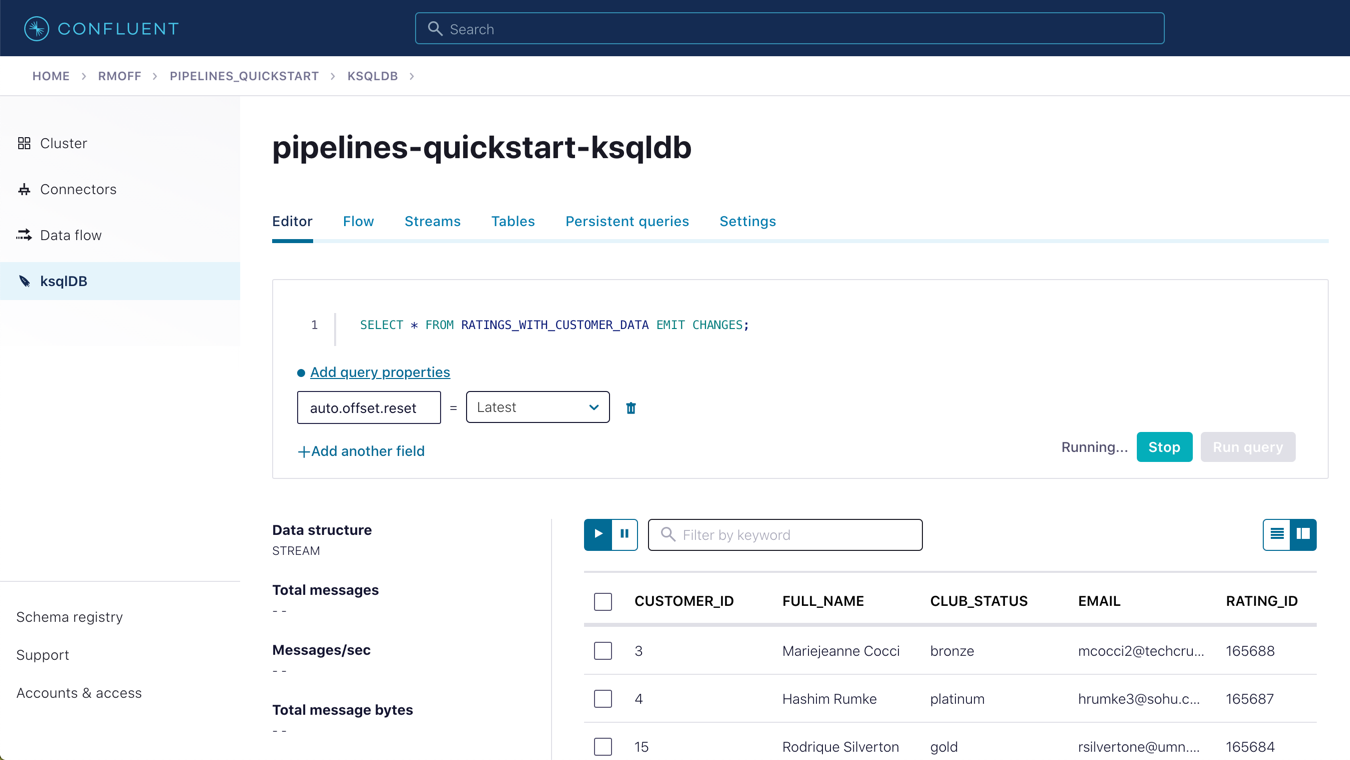
-
To show the power of streaming changes directly from the database, we’ll make a change to the customer data and observe how it is reflected in the enriched ratings data.
In the Confluent Cloud ksqlDB editor, run a query to show current ratings from customer ID 1. Because we only want current ratings, set the auto.offset.reset to latest. Note the value of CLUB_STATUS shown for each rating.
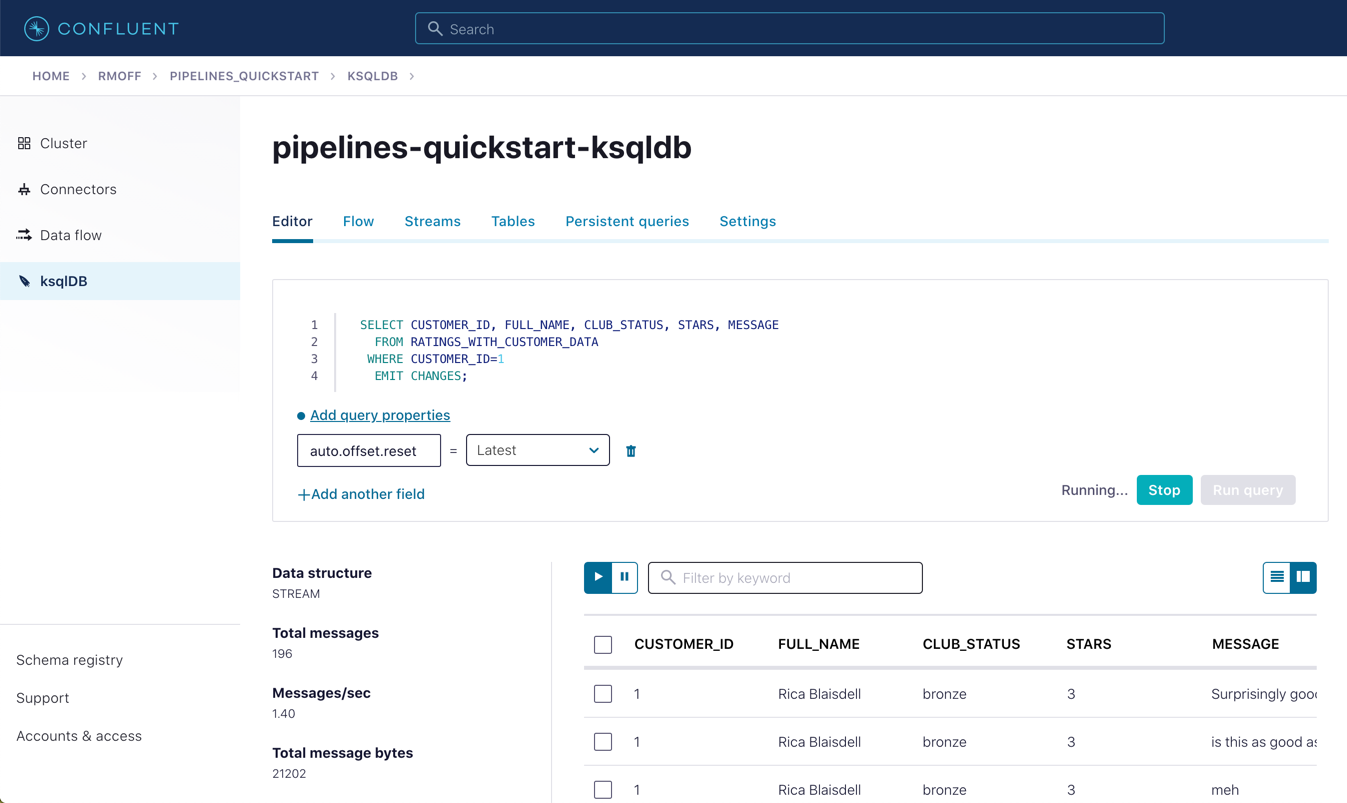
Leave the query running in the ksqlDB editor. In MySQL, make a change to the customer’s club status:
Note
Make sure that you run the UPDATE against the MySQL database, not ksqlDB.
UPDATE demo.CUSTOMERS SET CLUB_STATUS='platinum' WHERE ID=1;Watch the ksqlDB results table for subsequent ratings from customer ID 1. You should see that it soon reflects the updated CLUB_STATUS:
SELECT CUSTOMER_ID, FULL_NAME, CLUB_STATUS, STARS, MESSAGE FROM RATINGS_WITH_CUSTOMER_DATA WHERE CUSTOMER_ID=1 EMIT CHANGES;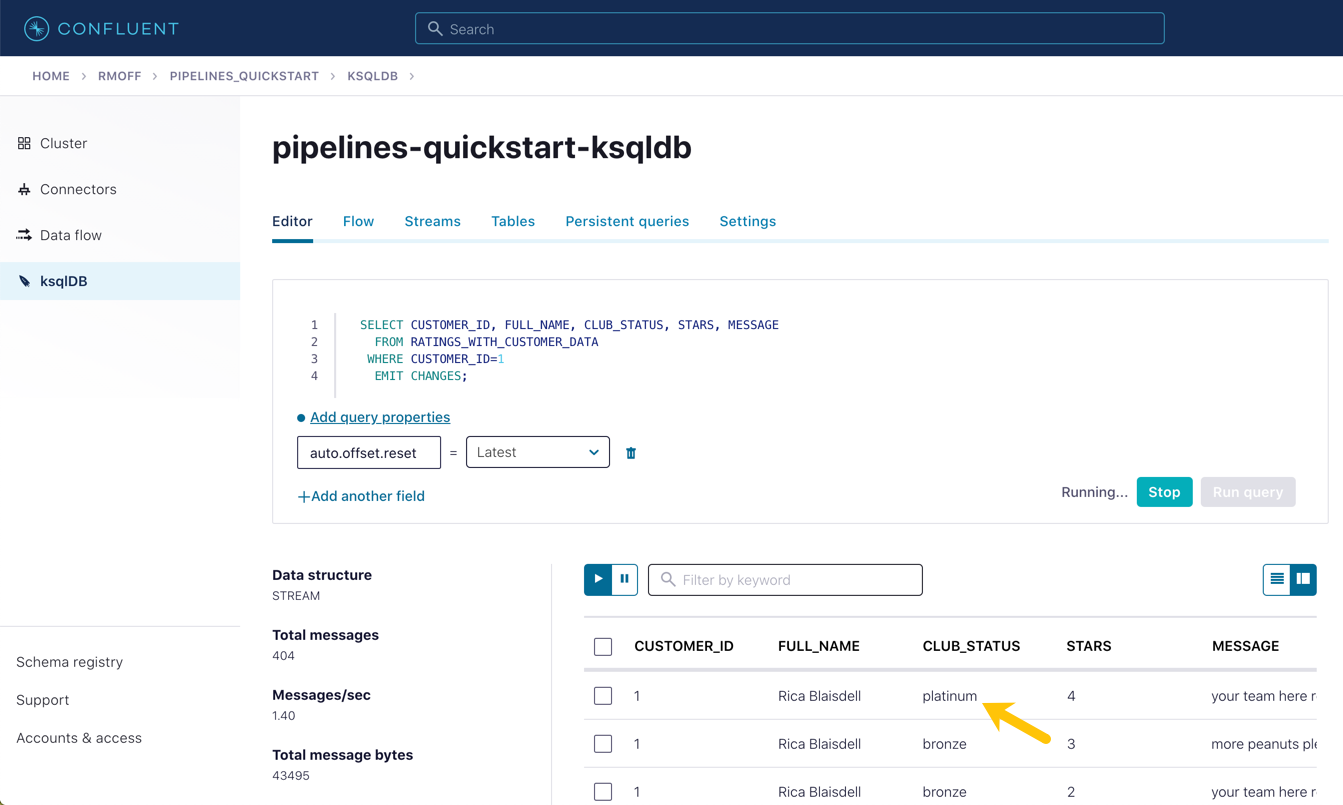
-
If you have data lineage enabled on your Confluent Cloud environment, go to the cluster’s "Topics" page, click on the ratings-enriched topic and then Data Lineage.
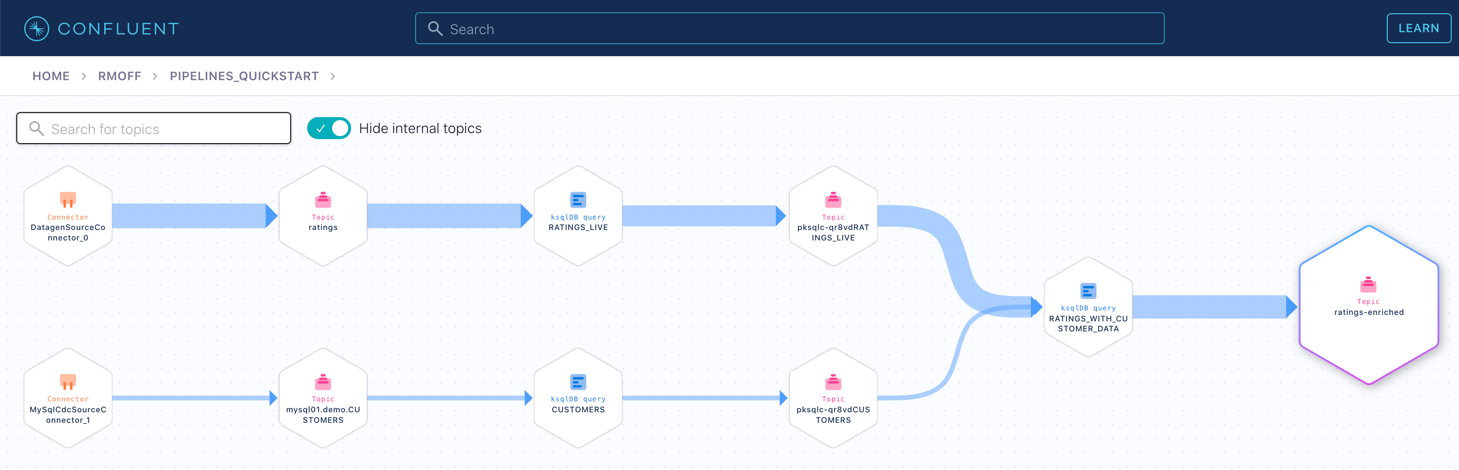
From here, you can see where the data comes from, its relative throughput volumes, and the stages of processing that it goes through.
Use the promo code PIPELINES101 & CONFLUENTDEV1 to get $25 of free Confluent Cloud usage and skip credit card entry.
Hands On: Joining Data Streams with ksqlDB
In the previous exercise, we filtered the ratings data coming from the data generator. Now, I wanna enrich that data with the customer entities with that customer table. To do that, first, we're gonna have to set up that customer topic that we're getting from the external MySQL database, we have to set that up as a table, we have to tell ksqlDB, that it's a table. And after that, we'll be able to do the join, the join like falls into place right away. Let's check it out. To create a new table, first, we create a stream over the Kafka topic the way we did before that should look familiar by now, then we're gonna create a table based on the stream, I wanna set the offset to earliest, so that we are sure to process all the records. This table is built as an aggregation of the stream using the latest by offset aggregation that you see in the query there. With the table built, we can now use it to enrich the rating stream that we've already got, we use a stream table join on the common key of user ID, that both the stream and the table have. Obviously, that's important, you can't do a join in a relational database without a common foreign key, so you do that same kind of thing here. Also, as an aside, when I had you create these topics, I said, hey, make sure they both have six partitions, that matters as well, we want these topics to be co-partitioned, same key, same number of partitions, and everything works out well if we do that. So first prototype to join with just a select, make sure that it works and returns the results that we're expecting and basically looks reasonable, which it does, each rating now includes information about the customer, which is cool. So we'll persist this to a new stream by prepending create stream to it the result of a stream table join is a stream. And now this is a persistent query, creating a new Kafka topic with the records, just like we did in the last exercise. Note that we're overriding the default Kafka topic name to a hard coded value, if we don't do this, the topic takes the name from the stream, plus an internal identifier prefix and it gets it gets a little messy, and we need this topic later on. So let's check that the new stream works, it looks good a live stream of events and as each event arrives, the customer information gets added to it. So looking at the live ratings stream for a particular user, how do we do that, so note their current club status, bronze imagine the customer status changes. It's not changed in Kafka, it's changed in the system in which the customer data is created, the database, right, that that MySQL database out there in the wilds of the internet. It's probably changed by an application, not a manual SQL UPDATE statement in practice, but work with me here. And notice how the next rating that comes in reflects the latest club status for the particular user. A minute ago, the event happened and it was joined to a bronze status and now it's an upgraded status and that event is is happening now and being joined to the current state of that customer in that table. ksqlDB has a data flow view, which is super cool. But if you want broader context, including where the data comes from, and goes to you wanna use the data lineage view. And as we start to create a more interesting pipeline that data lineage view becomes more and more useful. So we made a table we joined a stream to a table, absolutely fundamental activity in data pipelines and now you've done it.
Be the first to get updates and new content
We will only share developer content and updates, including notifications when new content is added. We will never send you sales emails. 🙂 By subscribing, you understand we will process your personal information in accordance with our Privacy Statement.






