Hands On: Confluent Cloud Schema Registry and Spring Boot

Viktor Gamov
Developer Advocate (Presenter)
Hands On: Confluent Cloud Schema Registry and Spring Boot
Note: This exercise is part of a larger course. You are expected to have completed the previous exercises.
The following continues with the program that you have worked on in previous exercises and begins with Confluent Cloud. Even though it continues from previous exercises, it has its own repo, which may be found on GitHub. (Refer there for a list of imports as well as an initial build.gradle file if you need them).
Set Up Schema Registry on Confluent Cloud
- On Confluent Cloud, select your environment, then Schema Registry. Select Set up on my own, then choose a cloud provider and region. Click Continue.
Add an Avro Gradle Plugin
-
Next, you’re going to use an Avro Gradle plugin from GitHub, which will allow you to create Java POJOs out of Avro schemas. In build.gradle, put the following in your “Plugins” section:
id "com.github.davidmc24.gradle.plugin.avro" version "1.2.0" -
If you are using IntelliJ (recommended for this exercise), also add the following:
id "idea"(in which case you will be able to see a new task).
-
Still in build.gradle, under “Dependencies,” add the following:
implementation 'org.apache.avro:avro:1.10.2' -
Then add this under “Repositories”:
mavenCentral() maven { url "https://packages.confluent.io/maven" } -
Finally, in settings.gradle,add the following at the top of the file:
pluginManagement { repositories { gradlePluginPortal() mavenCentral() } }
Create an Avro Schema and Generate Your POJOs
-
You will use a JSON-formatted Avro schema to generate your POJOs. Create a new folder in /src/main called “Avro.” In that folder, create a file called hobbit.avsc:
-
In the file, put a schema that represents the Hobbit object:
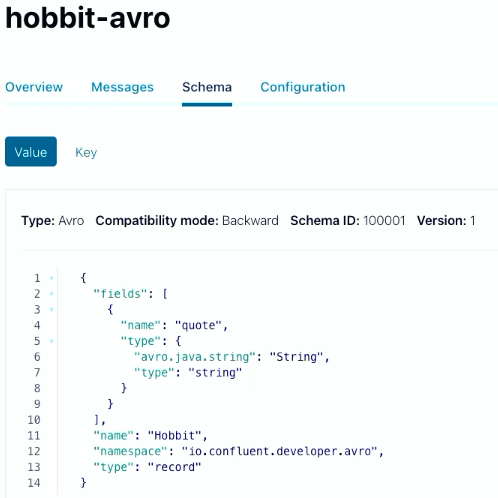
{ "fields": [ { "name": "quote", "type": { "avro.java.string": "String", "type": "string" } } ], "name": "Hobbit", "namespace": "io.confluent.developer.avro", "type": "record" }You’ll store a string with a quote from the Java Faker library, then wrap it into a Hobbit object.
-
Execute the Gradle task generateAvroJava, and in your Build directory, you should see a new folder called generated-main-avro-java that includes a Hobbit object. If you have enabled IntelliJ/Gradle generation, generated sources will be included in your classpath.
-
Note that you’re going to use a KafkaAvroSerializer that you need to add to build.gradle:
implementation "io.confluent:kafka-avro-serializer:6.1.0" -
In application.properties, you also need to specify the serializer (replacing the existing one):
spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer=io.confluent.kafka.serializers.KafkaAvroSerializer
Prepare Your Application
-
Now change the name of the topic in your producer:
Flux.zip(interval, quotes) .map(it -> template.send("hobbit-avro", faker.random().nextInt(42), it.getT2())).blockLast(); -
Then in your consumer, change the name of the topic as well as the types for ConsumerRecord:
@KafkaListener(topics = {"hobbit-avro"}, groupId = "spring-boot-kafka") public void consume(ConsumerRecord<Integer, Hobbit> record) { System.out.println("received = " + record.value() + " with key " + record.key()); } -
You won’t need a processor or REST API so comment out @Component from your Processor class and @RESTController, @RequiredArgsConstructor, and @GetMapping from your RestService class.
-
Now create a new topic in your application class:
@Bean NewTopic hobbit-avro() { return TopicBuilder.name("hobbit-avro").partitions(15).replicas(3).build(); }
Fetch Creds from Confluent Cloud
-
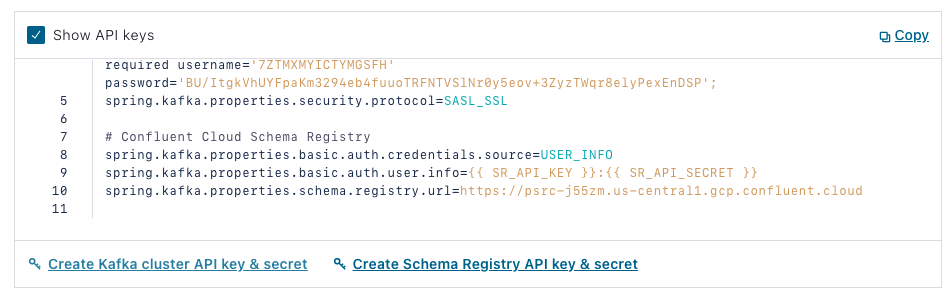
In Confluent Cloud, go to Cluster> Clients > Spring Boot > Create Schema Registry API key & secret:
-
Check the box, add a description, then select Continue, and your credentials will be entered into the config. Copy the section under “Confluent Cloud Schema Registry,” and return to your Java application and insert it into application.properties.
-
Note the Schema Registry URL, which is your endpoint, as well as the authentication properties.
Change Additional Application Parameters and Run
-
Now change the deserializers in application.properties for your consumer:
spring.kafka.consumer.key-deserializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.IntegerDeserializer spring.kafka.consumer.value-deserializer=io.confluent.kafka.serializers.KafkaAvroDeserializer -
Disable the @EnableKafkaStreams annotation.
-
Run the program, and you should see system.out.println writing data in Avro format. You will also see it in your topic in Confluent Cloud if you go to Topics > hobbit-avro > Messages. Values are stored in Avro format so the UI can’t display them.
-
You can also now see schema under your “Schema” tab on Confluent Cloud.
Delete Cluster
- This is the final exercise in the course, so make sure to delete your cluster. To do this, go to Cluster settings on the left-hand side menu, then click Delete cluster. Enter your cluster name, then select Continue.
Use the promo code SPRING101 to get $25 of free Confluent Cloud usage
Be the first to get updates and new content
We will only share developer content and updates, including notifications when new content is added. We will never send you sales emails. 🙂 By subscribing, you understand we will process your personal information in accordance with our Privacy Statement.


